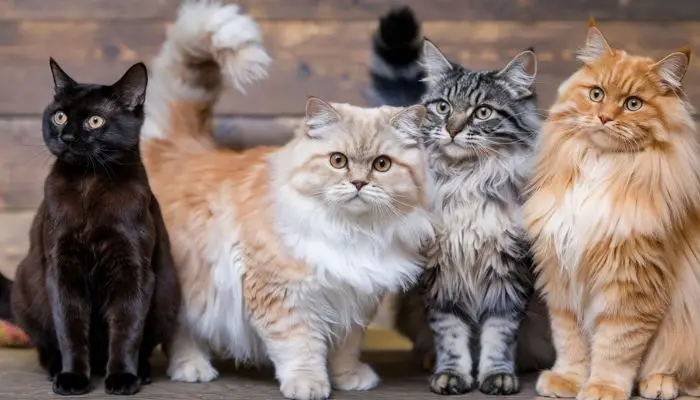
Cats are known for their diverse and stunning coat patterns, making each feline unique and intriguing. Understanding the different types of cat coats enhances our appreciation of these fascinating creatures and provides insights into their genetics, health, and grooming needs.
This guide delves into the variety of cat coats, highlighting the distinct patterns, textures, and colors that make each cat special.
Table of Contents
ToggleSummary
Cat coats come in various types, patterns, colors, and lengths. They range from single or double layers of fur to hairless bodies. Common patterns include tabby, bicolor, and colorpoint, while coat lengths vary from short to long. Each coat type requires specific care to keep it healthy and beautiful.
Understanding the Basics of Cat Coat Patterns
A cat’s coat pattern combines genetics, breed, and environmental factors. These patterns determine the visual appearance of the fur, including stripes, spots, or a single solid color. Below, we explore the primary categories of cat coat patterns:
1. Solid (Self) Coats
Solid-colored cats have uniform fur from root to tip without markings or variations. Common solid colors include:
- Black: A classic and elegant shade often associated with mystery.
- White: Pure and bright, white cats are rare and often carry genetic traits like heterochromia (different-colored eyes).
- Gray (Blue): A diluted black, this soft shade ranges from pale silver to dark charcoal.
- Orange (Red): Typically associated with male cats, this color can range from light ginger to deep red.
- Cream: A diluted form of orange, often appearing as a soft beige.
2. Tabby Pattern
Tabby is one of the most common and recognizable patterns, characterized by stripes, spots, or swirls. The distinct “M” shape easily identifies tabbies on their foreheads. The main types of tabby patterns are:
- Classic (Blotched) Tabby: Large swirling patterns that resemble a marble cake.
- Mackerel Tabby: Narrow, vertical stripes resembling a fish skeleton.
- Spotted Tabby: Instead of stripes, these cats have distinct spots of varying sizes.
- Ticked Tabby: Lacks stripes or spots but features agouti hairs, where each hair has bands of light and dark pigmentation.
3. Bicolor
Bicolor cats have a two-toned coat, often with white and another color, such as black or gray. Due to the distribution of the colors, this pattern is commonly referred to as a “tuxedo” when the cat appears to be wearing a formal suit.
4. Tricolor and Calico
Calico cats have a tri-color pattern, typically white, black, and orange. Unlike torties, calicos have distinct patches of color rather than a mixed pattern. There are variations of calico coats, such as:
- Dilute Calico: Features a softer version of the traditional calico colors, often including gray, cream, and light orange.
- Patched Tabby Calico: Combines tabby patterns with the classic calico color scheme.
5. Tortoiseshell (Tortie) Coats
Tortoiseshell cats, often simply called “torties,” have a unique blend of black and orange patches, giving them a mosaic-like appearance. Due to their genetic makeup, these cats are almost always female. Tortie coats can also include shades of cream, red, and blue, making them even more diverse.
6. Colorpoint
Colorpoint cats have a light body color with darker extremities—such as the ears, face, paws, and tail—creating a stunning contrast. Breeds like the Siamese, Balinese, and Himalayan are known for this pattern. The color contrast is temperature-dependent, with cooler areas of the body exhibiting darker hues.
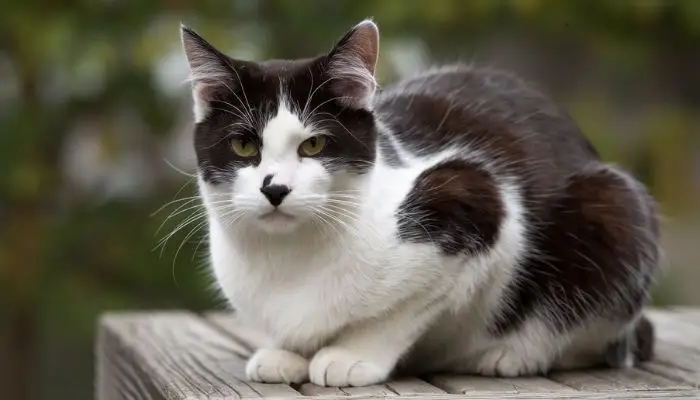

Exploring Cat Coat Colors
Beyond patterns, cats also exhibit a wide range of colors. Here are some of the most common and distinctive cat coat colors:
1. Black and White (Tuxedo) Cats
Tuxedo cats are predominantly black with distinctive white markings, often on the chest, belly, and paws, creating a “tuxedo” appearance. This classic pattern is highly popular and gives cats a dapper look.
2. Blue (Gray) Coats
The term “blue” in the cat world refers to shades of gray. Blue coats are often associated with certain breeds like the Russian Blue or British Shorthair, known for their soft, plush fur and gentle appearance.
3. Chocolate and Cinnamon
These less common colors are usually seen in specific breeds. Chocolate is a rich brown, while cinnamon is a lighter, warm brown shade. Both colors add depth and elegance to a cat’s appearance.
4. Fawn and Lilac
Fawn and lilac are diluted versions of cinnamon and chocolate, respectively. Fawn is a light, warm beige, while lilac is a soft grayish-pink. These colors are rare and typically found in purebred cats.

Types of Cat Coat Textures
The texture of a cat’s fur is another important aspect that varies significantly among breeds. Coat textures can affect grooming needs and how much a cat sheds. Below are the primary categories:
1. Short-Haired Cats
Short-haired cats have dense and smooth coats, making them easy to groom. They shed less than long-haired breeds and are popular among cat owners due to their low maintenance needs. Common short-haired breeds include the American Shorthair and the Bengal.
2. Long-Haired Cats
Long-haired cats have luxurious and flowing fur that can require regular grooming to prevent matting. They are known for their fluffy tails and impressive manes. Breeds like the Persian and Maine Coon are famous for their long-haired coats.
3. Curly Coats
Curly-coated cats have a unique texture due to a genetic mutation that affects the hair’s structure. The Devon and Selkirk Rex are notable for their curly fur, which feels soft and wavy. Curly coats are low-shedding but need specialized grooming.
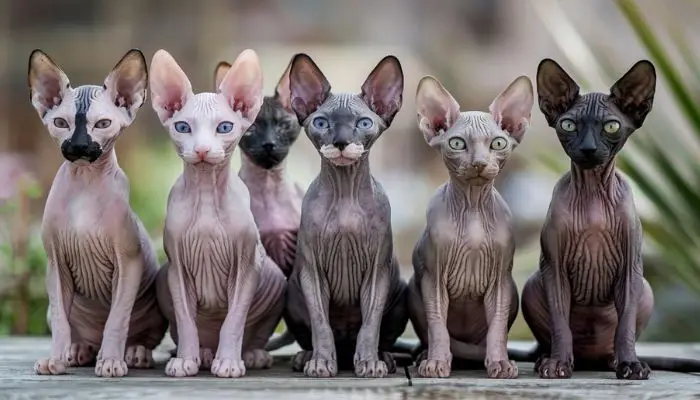
4. Hairless Cats
Although technically not “coated,” hairless cats like the Sphynx have a unique skin texture due to the lack of fur. These cats still require care, including regular bathing to remove oils that would typically be absorbed by fur.

Breed-Specific Coat Characteristics
Certain cat breeds are renowned for their unique coat patterns and textures. Below are some examples:
1. Persian Cats
Persians are known for their long, thick fur, which requires daily grooming. Their coats come in various colors and patterns, from solid black to silver-shaded.
2. Siamese Cats
The Siamese is famous for its point coloration, a pattern where the ears, face, paws, and tail are darker than the rest of the body. This unique coat develops due to temperature-sensitive pigmentation.
3. Bengal Cats
Bengals have a distinctive spotted or marbled coat resembling a wild leopard. Their fur is short and dense, often with a shimmering quality known as “glitter.”
4. Scottish Fold
Known for their folded ears, Scottish Folds have a plush, soft coat that can be short or long. Their coats are available in many colors and patterns, making them a visually diverse breed.
Grooming Tips for Different Cat Coats
Proper grooming is essential for maintaining the health and beauty of a cat’s coat. Here are some tips based on coat type:
1. Short-Haired Cats: Regular weekly brushing helps remove loose fur and reduces shedding.
2. Long-Haired Cats: Daily brushing prevents matting and tangles. For best results, use a wide-tooth comb and a slicker brush.
3. Curly Coats: Curly-coated cats benefit from gentle brushing to avoid damaging their unique texture. Specialized brushes are recommended.
4. Hairless Cats: Hairless cats require weekly baths to clean their skin. Use a gentle, hypoallergenic shampoo to prevent irritation.
Conclusion
Cat coats are as diverse as the felines themselves, showcasing a range of patterns, colors, and textures that make each cat unique. Whether it’s the striking stripes of a tabby, the vibrant patches of calico, or the smooth shine of a solid coat, understanding these differences helps us appreciate the beauty and complexity of our feline companions. Proper grooming tailored to each coat type ensures a healthy, happy cat, allowing us to enjoy their beauty to the fullest.
FAQs
Hairlessness is caused by a genetic mutation, most commonly found in the Sphynx breed.
No cat is completely hypoallergenic, but some breeds, like the Siberian, produce fewer allergens.
Regular brushing and a healthy diet can minimize shedding.
Yes, factors like aging and sunlight can alter a cat’s coat color over time.
The Lykoi’s “werewolf” pattern is one of the rarest in the world.